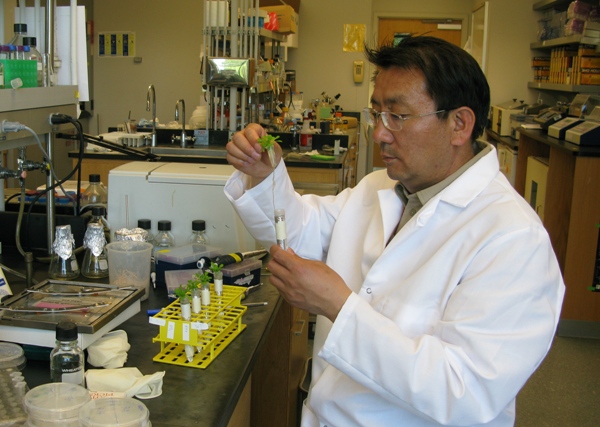
王锁民
【来源:草地农业科技学院 | 发布日期:2018-01-02 | 作者:办公室 】

一、 个人简况
王锁民,男,博士,二级教授,博士生导师。主要从事草类植物逆境生理与基因工程及荒漠草原恢复治理方面的研究工作。现任bet365亚洲版官网草类植物逆境生理与遗传改良研究所所长、“农业部草地农业生态系统重点开放实验室”副主任,甘肃省植物生理学会副理事长,教育部高校草学类专业教学指导委员会秘书长,中国草学会草业生物技术委员会副理事长,中国草学会牧草育种委员会副主任,中国草学会草业教育委员会副主任,中国草学会理事,甘肃省重大项目建设管理咨询专家;“风沙危害区生态修复与沙产业协同创新中心”常务理事;《兰州大学学报》(自然科学版)、《植物生态学报》、《草业学报》、《草业科学》和《草业与畜牧》编委。2005年入选“教育部新世纪优秀人才支持计划”;2009年入选“甘肃省领军人才”(第二层次);2010年获民勤生态治理优秀个人“科技进步奖”; 获感动甘肃2012年“十大陇人骄子”提名奖;2012年享受国务院政府特殊津贴。近年主持国家自然科学基金项目、国家农业科技成果转化项目、国家863计划、国家973项目子课题等科研项目共21项。获省部级自然科学一等奖1项、科技进步二等奖2项、三等奖4项;获国家发明专利5项;以第一作者或通讯作者在Plant Physiology; Plant Journal; Plant Biotechnology Journal ; Plant, Cell and Environment; Annals of Botany 和Plant and Soil等刊物发表论文159篇,其中49篇被SCI收录、9篇被EI收录、77篇被CSCD收录;参编著作2部。二、 研究方向
植物逆境生理与分子生物学、牧草营养生理与基因工程。
三、 学术论文、专利及获奖情况
(姓名下划线者为通讯作者)
代表性学术论文
<1> Ma Q., Hu J., Zhou X.R., Yuan H.J., Kumar T., Luan S., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2017) ZxAKT1 is essential for K+ uptake and K+/Na+ homeostasis in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Plant Journal, 90: 48-60. (IF2014= 6.09).
<2> Ma Q., Bao A.K., Chai W.W., Wang W.Y., Zhang J.L., Li Y.X., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2016) Transcriptomic analysis of the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum in response to salt treatment and osmotic stress. Plant and Soil, 402:343-361. (IF2014= 2.952).
<3> Bao A.K., Du B.Q., Touil L., Kang P., Wang Q.L., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2016) Co-expression of tonoplast Cation/H+ antiporter and H+-pyrophosphatase from xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum improves alfalfa plant growth under salinity, drought, and field conditions. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 14:964-975. (IF2014= 5.752).
<4> Duan H.R., Ma Q., Zhang J.L., Hu J., Bao A.K., Wei L., Wang Q., Luan S., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2015) The inward-rectifying K+ channel SsAKT1 is a candidate involved in K+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda salsa under saline condition. Plant and Soil, 395:173-187. (IF2014= 2.952).
<5> Yuan H.J., Ma Q., Wu G.Q., Wang P., Hu J., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2015) ZxNHX controls Na+ and K+ homeostasis at the whole-plant level in Zygophyllum xanthoxylum through feedback regulation of the expression of genes involved in their transport. Annals of Botany, 115:495-507 (IF2014= 3.654).
<6> Ma Q., Li Y.X., Yuan H.J., Hu J., Wei L., Bao A.K., Zhang J.L., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2014) ZxSOS1 is essential for long-distance transport and spatial distribution of Na+ and K+ in the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Plant and Soil, 374: 661-676 (IF2014= 2.952).
<7> Zhang J.L., Flowers T.J., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2013) Differentiation of low-affinity Na+ uptake pathways and kinetics of the effects of K+ on Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant and Soil, 368: 629-640 (IF2014= 2.952).
<8> Guo Q., Wang P., Ma Q., Zhang J.L., Bao A.K., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2012) Selective transport capacity for K+ over Na+ is linked to the expression levels of PtSOS1 in halophyte Puccinellia tenuiflora. Functional Plant Biology, 39: 1047-1057 (IF2014= 3.145).
<9> Ma Q., Yue L.J., Zhang J.L., Wu G.Q., Bao A.K., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2012) Sodium chloride improves photosynthesis and water status in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Tree Physiology, 32:4-13 (IF2014= 3.655).
<10> Zhang J.L., Flowers T.J., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2010). Mechanisms of sodium uptake by roots of higher plants. Plant and Soil, 326: 45-60 (IF2014= 2.952).
<11> Wang C.M., Zhang J.L., Liu X.S., Li Z., Wu G.Q., Cai J.Y., Flowers T.J., Wang S.M.(王锁民) (2009) Puccinellia tenuiflora maintains a low Na+ level under salinity by limiting unidirectional Na+ influx resulting in a high selectivity for K+ over Na+. Plant, Cell and Environment, 32: 486-496 (IF2014= 6.96).
<12> Wang S.M.(王锁民), Zhang J.L., Flowers T.J. (2007) Low-affinity Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant Physiology, 145:559-571 (IF2014= 6.841).
<1> 王锁民, 岳利军, 冯波 (2009). 国家发明专利:促进白刺种子萌发的方法. 授权号: ZL200710018697.5.
<2> 王锁民, 周向睿, 岳利军 (2011). 国家发明专利:钠复合肥及其应用和施用方法. 授权号: ZL200710018840.0.
<3> 王锁民, 席杰军, 伍国强, 王燕雯(2012). 国家发明专利:一种利用荒漠旱生植物霸王H+-PPase和液泡膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因培育耐盐抗旱百脉根的方法. 授权号: ZL 201010166976.8.
<4> 王锁民, 席杰军, 伍国强, 王燕雯(2012). 国家发明专利:强旱生植物霸王液泡膜氢焦磷酸酶基因和植物表达载体及其植株遗传转化方法. 授权号: ZL201010120239.4
获奖情况
<1> 2011年获甘肃省自然科学一等奖:荒漠草原典型盐生植物适应逆境的机理研究,第一获奖人。
<3> 2007年获甘肃省科技进步二等奖:黄土高原半干旱区(定西)高效生态农业研究与示范,第七获奖人。
<4> 2005年获甘肃省科技进步二等奖:河西走廊山地绿洲荒漠系统耦合机理与优化耦合模式研究,第六获奖人。
<5> 2004年获甘肃省科技进步三等奖:河西走廊盐渍化草地综合改良与持续高效利用技术研究,第五获奖人。
<6> 1999年获甘肃省科技进步三等奖:草坪草生长化学调控研究,第三获奖人。
<7> 1998年获农业部科技进步三等奖:暖季型草坪草种子种苗生产和建坪管理技术,第十四获奖人。
<8> 1998年获甘肃省科技进步三等奖:河西走廊荒漠绿洲交错区草地培育优化生态模式研究,第五获奖人。
四、 承担科研项目
主持的主要科研项目
(1) 国家自然科学基金重点项目 (批准号:31730093),起止年月:2018年1月-2022年12月。
(2) 国家自然科学基金项目 (批准号:31470503),起止年月:2015年1月-2018年12月。
(3) 国家重点基础研究发展规划(973)项目(批准号:2014CB138701-3)子课题,起止年月:2014年1月-2018年8月。
(4) 教育部博士点基金优先发展领域项目(批准号:20130211130001),起止年月:2014年1月-2016年12月。
(5) 国家农业科技成果转化资金项目(批准号:2013GB2G100482),起止年月:2013年6月-2015年12月。
(6) 国家自然科学基金项目(批准号:31170431),起止年月:2012年1月-2015年12月。
(7) 国家自然科学基金项目(批准号:31072073),起止年月:2011年1月-2013年12月。
(8) 国家农业科技成果转化资金项目(批准号:2009GB23600512),起止年月:2009年6月-2011年6月。
(9) 高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金项目(批准号:20090211110001),起止年月:2010年1月-2012年12月。
(10)国家重点基础研究发展规划(973)项目(批准号:2007CB108901)专题,起止年月:2007年7月-2011年8月。
(11)国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划) 项目(批准号:2006AA10Z126),起止年月:2006年12月-2010年10月。
(12)“十一五”国家科技支撑计划重点项目(批准号:2008BADB3B01)子课题,起止年月:2008年1月-2010年12月。
(13)国家自然科学基金项目 (批准号:30770347),起止年月:2008年1月-2010年12月。
(14)国家自然科学基金项目 (批准号:30671488),起止年月:2007年1月-2009年12月。
(15)英国皇家学会中英合作项目(批准号:IJP-2005/R2),起止年月:2006年1月-2007年12月。
(16)甘肃省农业生物技术研究与开发项目 (批准号:GNSW-2004-07),起止年月:2004年12月-2007年12月。
(17)国家自然科学基金项目 (批准号:30270947),起止年月:2003年1月-2005年12月。
(18)国家重点基础研究发展规划(973)项目(批准号:G1999011705)专题,起止年月:2001年7月-2004年9月。
(19)科技部重大基础研究前期研究专项(批准号:2002CCC01600),起止年月:2003年1月-2004年12月。
(20)国家科技攻关计划(批准号:2001BA901A18)子课题,起止年月:2002年1月-2004年12月。
(21)国家自然基金委对外交流与合作项目(批准号:国科金外资助字第30511130606号),起止年月:2006年1月-2006年8月。
(22)科技部中澳(大利亚)科技合作特别资金项目(批准号:国科外字[2000]第0273号),起止年月:2001年1月-2002年12月。
所获人才基金项目
(1) 教育部“新世纪优秀人才支持计划”项目 (批准号:NCET-05-0882),起止年月:2006年1月-2008年12月。
(2) 中国博士后科学基金项目,起止年月:1999年9月-2001年3月。
(3) 甘肃省“333科技人才工程培养计划,起止年月:2001年1月-2003年12月。
五、学习与工作经历
学历
1983.9~1987.6 西北师范大学生物系,生物学专业,获理学学士学位。
1987.9~1990.6 首都师范大学(原北京师范学院)生物系,植物生理学专业,获理学硕士学位,导师为赵微平教授和赵思齐教授。
1995.9~1998.6 甘肃农业大学草业学院,草业科学专业,获农学博士学位,导师为任继周院士和胡自治教授。
主要科研工作经历
2004.6~至今: bet365亚洲版官网教授;2005年6月聘为博士研究生指导教师。
2017.8~2018.2:加拿大卡尔顿大学生物系及生物化学研究所(Department of Biology and Institute of Biochemistry)访问教授,合作者为Owen Rowland教授。
2008.8~2009.7:美国加州大学伯克利分校(University of California-Berkeley)植物与微生物系访问学者,合作导师为Sheng Luan教授。
2003.2~2004.2:获英国皇家学会奖学金资助,于苏塞克斯大学(University of Sussex)生命科学院进行合作研究,合作导师为Tim Flowers教授。
2000.9~2004.5:bet365亚洲版官网、生命科学学院副教授。
1998.8~2002.3:甘肃草原生态研究所副研究员。
1999.9~2000.8:在中国科学院上海植物生理生态研究所植物分子遗传国家重点实验室开展合作研究工作。
1998.7~1999.8:于兰州大学生命科学院进行博士后研究工作,合作导师为张承烈教授。
1993.9~1995.8:甘肃草原生态研究所助理研究员。
1990.6~1993.8:甘肃草原生态研究所研究实习员。
通讯地址:
甘肃省兰州市嘉峪关西路768号,bet365亚洲版官网
邮编: 730020
实验室及办公地点:兰州市天水南路222号,邮编: 730000
兰州大学盘旋路校区逸夫生物楼4层
Email: smwang@lzu.edu.cn
传真: 0931-8910979
电话: 0931-8910983(办); 0931-8913447(实验室)
Prof. Suo-Min Wang is the director of the Institute of Herbaceous Plant Stress Physiology and Genetic Improvement, State Key Laboratory of Grassland Agro-ecosystems and College of Pastoral Agriculture Science and Technology, Lanzhou University. He obtained his PhD (1998) in Gansu Agricultural University, China, and had worked in Lanzhou University where he has remained successively as an assistant, lecturer, associate Professor and Professor. He had been to the National Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics, Shanghai Institute of Plant Physiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences as a research visitor, and School of Life Sciences in Lanzhou University as a postdoctoral fellow. He had visited Prof. Tim Flowers’ Lab at School of Life Sciences, University of Sussex in the UK as a research fellow supported by the Sino-British Fellowship Trust Award of the Royal Society of the UK, and Prof. Sheng Luan’s Lab at University of California-Berkeley in the USA as a visiting scholar for one year, respectively. He had also been to Prof. Owen Rowland’s Lab at the Department of Biology and Institute of Biochemistry, Carleton University in Canada as visiting Professor for six months.
Prof. Wang has been elected as the New Century Excellent Talents in University from the Ministry of Education of China (2005) and the Leading Talent in Gansu Province (second level, 2009), enjoyed Special government allowances of the State Council, China (2012), and has received important academic awards and honors, including Vice Director of Pratacultural Education Committee of Chinese Grassland Society (2006), Vice Director of Forage Breeding Committee of Chinese Grassland Society (2009), the first prize of Natural Science in Gansu Province (2011), Vice President of the Grass Biotechnology Committee of Chinese Grassland Society (2013) and the secretary-general of University Teaching Guidance Committee of Pratacultural Science Specialty, the Ministry of Education of China (2013) etc.
Currently Prof. Wang’s lab main research interests concern plant abiotic stress physiology and molecular biology, and the genetic improvement of stress tolerance in forages. He has published over 60 papers in international journals including Plant Journal, Plant Physiology, Plant Biotechnology Journal, Plant Cell and Environment, Annals of Botany, Tree Physiology, and Plant and Soil etc.
Address:768 West Jiayuguan Road, Lanzhou 730020, P.R.China
State Key Laboratory of Grassland Agro-ecosystems,
College of Pastoral Agriculture Science and Technology,
Lanzhou University
Telephone:86-931-8910983(O); 86-931-8913447(lab)
Fax: 86-931-8910979
E-mail: smwang@lzu.edu.cn
State Key Laboratory of Grassland Agro-ecosystems,
College of Pastoral Agriculture Science and Technology,
Lanzhou University
Telephone:86-931-8910983(O); 86-931-8913447(lab)
Fax: 86-931-8910979
E-mail: smwang@lzu.edu.cn
MAIN PUBLICATIONS (2002- Present):*Corresponding author
Ma Q., Hu J., Zhou X.R., Yuan H.J., Kumar T., Luan S., *Wang S.M. (2017) ZxAKT1 is essential for K+ uptake and K+/Na+ homeostasis in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Plant Journal, 90: 48-60.
Ma Q., Bao A.K., Chai W.W., Wang W.Y., Zhang J.L., Li Y.X., *Wang S.M. (2016) Transcriptomic analysis of the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum in response to salt treatment and osmotic stress. Plant and Soil, 402:343-361.
Bao A.K., Du B.Q., Touil L., Kang P., Wang Q.L., *Wang S.M. (2016) Co-expression of tonoplast Cation/H+ antiporter and H+-pyrophosphatase from xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum improves alfalfa plant growth under salinity, drought, and field conditions. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 14:964-975.
Duan H.R., Ma Q., Zhang J.L., Hu J., Bao A.K., Wei L., Wang Q., Luan S., *Wang S.M. (2015) The inward-rectifying K+ channel SsAKT1 is a candidate involved in K+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda salsa under saline condition. Plant and Soil, 395:173-187.
Yuan H.J., Ma Q., Wu G.Q., Wang P., Hu J., *Wang S.M. (2015). ZxNHX controls Na+ and K+ homeostasis at the whole-plant level in Zygophyllum xanthoxylum through feedback regulation of the expression of genes involved in their transport. Annals of Botany, 115: 495-507.
Ma Q., Tang R.J., Zheng X.J., *Wang S.M., Luan S. (2015) The calcium sensor CBL7 modulates plant responses to low nitrate in Arabidopsis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 468:59-65.
Wang P, Guo Q, Wang Q, Zhou XR, *Wang S.M. (2015) PtAKT1 maintains selective absorption capacity for K+ over Na+ in halophyte Puccinellia tenuiflora under salt stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2015, 37:1-10
Wang Q., Guan C., Wang P., Lv M.L., Ma Q., Wu G.Q., Bao A.K., Zhang J.L., *Wang S.M. (2015). AtHKT1;1 and AtHAK5 mediate low-affinity Na+ uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana under mild salt stress. Plant Growth Regulation, 75:615-623.
Niu S.Q., Li H.R., Paré P.W., Aziz M., Wang S.M., Shi H.Z., Li J., Han Q.Q., Guo S.Q., Li J., Guo Q., Ma Q. (2015) Zhang JL. Induced growth promotion and higher salt tolerance in the halophyte grass Puccinellia tenuiflora by beneficial rhizobacteria. Plant and Soil, doi: 10.1007/s11104-015-2767-z
Wu Y.N., Feng Y.L., Paré P.W., Chen Y.L., Xu R., Wu S., Wang S.M., Zhao Q., Li H.R., Wang Y.Q., Zhang J.L. (2015) Beneficial soil microbe Bacillus subtilis (GB03) promotes seed germination, growth and photosynthesis in Codonopsis pilosula. Crop & Pasture Science, doi: 10.1071/CP15110.
Ma Q., Li Y.X., Yuan H.J., Hu J., Wei L., Bao A.K., Zhang J.L., *Wang S.M. (2014). ZxSOS1 is essential for long-distance transport and spatial distribution of Na+ and K+ in the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Plant and Soil, 374: 661-676.
Bao A.K., Wang Y.W., Xi J.J., Liu C., Zhang J.L., *Wang S.M. (2014). Co-overexpression of xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum ZxNHX and ZxVP1-1 enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Lotus corniculatus by increasing cations accumulation. Functional Plant Biology, 41: 203-214.
Wang Q., Guan C., *Wang S.M. (2014). Coordination of AtHKT1;1 and AtSOS1 facilitates Na+ and K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana under salt stress. Journal of Plant Biology, 57: 282-290.
Han Q.Q., Lü X.P., Bai J.P., Qiao Y., Paré P.W., Wang S.M., Zhang J.L., Wu Y.N., Pang X.P., Xu W.B., Wang Z.L. (2014). Beneficial soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis (GB03) augments salt tolerance of white clover. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5: 525
Zhang J.L., Aziz M., Qiao Y., Han Q.Q., Li J., Wang Y.Q., Shen X., Wang S.M., Paré P.W. (2014). Soil microbe Bacillus subtilis (GB03) induces biomass accumulation and salt tolerance with lower sodium accumulation in wheat. Crop and Pasture Science, 65: 423-427
Zhang J.L., Flowers T.J., *Wang S.M. (2013) Differentiation of low-affinity Na+ uptake pathways and kinetics of the effects of K+ on Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant and Soil, 368: 629-640.
Kang J.J., Duan J.J., *Wang S.M., Zhao M., Yang Z.H. (2013). Na compound fertilizer promotes growth and enhances drought resistance of the succulent xerophyte Haloxylon ammodendron. Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 59:289-299.
Guo Q., Wang P., Ma Q., Zhang J.L., Bao A.K., *Wang S.M. (2012) Selective transport capacity for K+ over Na+ is linked to the expression levels of PtSOS1 in halophyte Puccinellia tenuiflora. Funct Plant Biol, 39: 1047-1057.
Ma Q., Yue L.J., Zhang J.L., Wu G.Q., Bao A.K., *Wang S.M. (2012) Sodium chloride improves photosynthesis and water status in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Tree Physiology, 32: 4-13.
Wu G.Q., Xi J.J., Wang Q., Bao A.K., Ma Q., Zhang J.L., *Wang S.M. (2011). The ZxNHX gene encoding tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter from the xerophytes Zygophyllum xanthoxylum plays important roles in response to salt and drought. Journal of Plant Physiology, 168: 758-767.
Lan W.Z., Wang W., Wang S.M., Li L.G., Buchanan B.B., Lin H.X., Gao J.P., Luan S. (2010). A rice high-affinity potassium transporter (HKT) from rice conceals a calcium-permeable cation channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107: 7089-7094.
Zhang J.L., Flowers T.J., *Wang S.M. (2010). Mechanisms of sodium uptake by roots of higher plants. Plant and Soil, 326:45-60.
Wang C.M., Zhang J.L., Liu X.S., Li Z., Wu G.Q., Cai J.Y., Flowers T.J., *Wang S.M. (2009) Puccinellia tenuiflora maintains a low Na+ level under salinity by limiting unidirectional Na+ influx resulting in a high selectivity for K+ over Na+. Plant, Cell and Environment, 32: 486-496.
Bao A.K., *Wang S.M., Wu G.Q., Xi J.J., Zhang J.L., Wang C.M. (2009) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis H+-PPase enhanced resistance to salt and drought stress in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Science, 176: 232-240.
Bao A.K., Guo Z.G., Zhang H.F., *Wang S.M. (2009). A procedure for assessing the salt tolerance of lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) cultivar seedlings by combining agronomic and physiological indicators. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 52: 435-443.
Wang S.M., Zhang J.L., *Flowers T. J. (2007) Low-affinity Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant Physiology 145: 559-571
Zhang H.F., *Wang S.M. (2007) Advances in study of Na+ uptake and transport in higher plants and Na+ homeostasis in the cell. Chinese Bulletin of Botany 24:561-571 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gong H. J., Zhu X. Y., Chen K. M., *Wang S.M., Zhang C. L. (2005) Silicon alleviates oxidative damage of wheat plants in pots under drought. Plant Science 169: 313-321
Zhu X. Y., Gong H. J., Chen G. C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C. L. (2005) Different solute levels in two spring wheat cultivars induced by progressive field water stress at different developmental stages. Journal of Arid Environments 62:1-14
*Wang S.M., Zhao G.Q., Gao Y.S., Tang Z.C., Zhang C.L. (2004) Puccinellia tenuiflora exhibits stronger selectivity for K+ over Na+ than wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition 27: 1841-1857
*Wang S.M., Wan C.G., Wang Y.R., Chen H., Zhou Z.Y., Fu H., Sosebee R.E. (2004) The Characteristics of Na+, K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. Journal of Arid Environments 56:525-539
Peng Y. H., Zhu Y. F., Mao Y. Q., Wang S.M., Su W. A., Tang Z.C. (2004) Alkali grass resists salt stress through high [K+] and an endodermis barrier to Na+. Journal of Experiment Botany 55: 939-949
Chen K.M., Gong H.J., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2004) The regulation of the plasma membrane redox system and H+-transport in adaptation of reed ecotypes to their habitats. Biologia Plantarum 48:87-92
Jing Y., Gong H.J., Zhao Z.G., Chen G.C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2004) Gradual drought under field conditions influences the glutathione metabolism, redox balance and energy supply in spring wheat. Acta Botanica Sinica 46:1040-1048
Chen K.M., Gong H.J., Chen G.C., Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2004) Gradual drought under field conditions influences the glutathione metabolism, redox balance and energy supply in spring wheat. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 23:20-28
Xing H., Tan L.L., An L.Z., Zhao Z.G., Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2004) Evidence for the involvement of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in osmotic stress tolerance of wheat seedlings: Inverse correlation between leaf abscisic acid accumulation and leaf water loss. Plant Growth Regulation 42:61-68
Gong H.J., Chen K.M., Chen G.C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Effects of silicon on growth of wheat under drought. Journal of Plant Nutrition 26:1055-1063
Gong H.J., Chen K.M., Chen G.C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Drought stress stimulates p-nitrophenyl phosphate hydrolysis rate of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase from wheat leaves. Plant Growth Regulation 40:139-145
Gong H.J., Chen K.M., Chen G.C., Zhao Z.G., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Redox system in the plasma membranes of two ecotypes of reed (Phragmites communis Trin.) leaves from different habitats. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 32:163-168
Zhu X.Y., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Composition and characteristic difference in photosynthetic membranes of two ecotypes of reed (Phragmites communis ) from different habitats. Photosynthetica 41:97-104
Zhu X.Y., Jing Y., Chen G.C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Solute levels and osmoregulatory enzyme activities in reed plants adapted to drought and saline habitats. Plant Growth Regulation 41:165-172
Chen K.M., Gong H.J., Chen G.C., Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Up-regulation of glutathione metabolism and changes in redox status involved in adaptation of reed (Phragmites communis Trin.) ecotypes to drought-prone and saline habitats. Journal of Plant Physiology 160: 293-301
*Wang S.M., Zheng W.J., Ren J.Z., Zhang C.L. (2002) Selectivity of various types of salt-resistant plants for K+ over Na+. Journal of Arid Environments 52:457-472
Ma Q., Hu J., Zhou X.R., Yuan H.J., Kumar T., Luan S., *Wang S.M. (2017) ZxAKT1 is essential for K+ uptake and K+/Na+ homeostasis in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Plant Journal, 90: 48-60.
Ma Q., Bao A.K., Chai W.W., Wang W.Y., Zhang J.L., Li Y.X., *Wang S.M. (2016) Transcriptomic analysis of the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum in response to salt treatment and osmotic stress. Plant and Soil, 402:343-361.
Bao A.K., Du B.Q., Touil L., Kang P., Wang Q.L., *Wang S.M. (2016) Co-expression of tonoplast Cation/H+ antiporter and H+-pyrophosphatase from xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum improves alfalfa plant growth under salinity, drought, and field conditions. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 14:964-975.
Duan H.R., Ma Q., Zhang J.L., Hu J., Bao A.K., Wei L., Wang Q., Luan S., *Wang S.M. (2015) The inward-rectifying K+ channel SsAKT1 is a candidate involved in K+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda salsa under saline condition. Plant and Soil, 395:173-187.
Yuan H.J., Ma Q., Wu G.Q., Wang P., Hu J., *Wang S.M. (2015). ZxNHX controls Na+ and K+ homeostasis at the whole-plant level in Zygophyllum xanthoxylum through feedback regulation of the expression of genes involved in their transport. Annals of Botany, 115: 495-507.
Ma Q., Tang R.J., Zheng X.J., *Wang S.M., Luan S. (2015) The calcium sensor CBL7 modulates plant responses to low nitrate in Arabidopsis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 468:59-65.
Wang P, Guo Q, Wang Q, Zhou XR, *Wang S.M. (2015) PtAKT1 maintains selective absorption capacity for K+ over Na+ in halophyte Puccinellia tenuiflora under salt stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2015, 37:1-10
Wang Q., Guan C., Wang P., Lv M.L., Ma Q., Wu G.Q., Bao A.K., Zhang J.L., *Wang S.M. (2015). AtHKT1;1 and AtHAK5 mediate low-affinity Na+ uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana under mild salt stress. Plant Growth Regulation, 75:615-623.
Niu S.Q., Li H.R., Paré P.W., Aziz M., Wang S.M., Shi H.Z., Li J., Han Q.Q., Guo S.Q., Li J., Guo Q., Ma Q. (2015) Zhang JL. Induced growth promotion and higher salt tolerance in the halophyte grass Puccinellia tenuiflora by beneficial rhizobacteria. Plant and Soil, doi: 10.1007/s11104-015-2767-z
Wu Y.N., Feng Y.L., Paré P.W., Chen Y.L., Xu R., Wu S., Wang S.M., Zhao Q., Li H.R., Wang Y.Q., Zhang J.L. (2015) Beneficial soil microbe Bacillus subtilis (GB03) promotes seed germination, growth and photosynthesis in Codonopsis pilosula. Crop & Pasture Science, doi: 10.1071/CP15110.
Ma Q., Li Y.X., Yuan H.J., Hu J., Wei L., Bao A.K., Zhang J.L., *Wang S.M. (2014). ZxSOS1 is essential for long-distance transport and spatial distribution of Na+ and K+ in the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Plant and Soil, 374: 661-676.
Bao A.K., Wang Y.W., Xi J.J., Liu C., Zhang J.L., *Wang S.M. (2014). Co-overexpression of xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum ZxNHX and ZxVP1-1 enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Lotus corniculatus by increasing cations accumulation. Functional Plant Biology, 41: 203-214.
Wang Q., Guan C., *Wang S.M. (2014). Coordination of AtHKT1;1 and AtSOS1 facilitates Na+ and K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana under salt stress. Journal of Plant Biology, 57: 282-290.
Han Q.Q., Lü X.P., Bai J.P., Qiao Y., Paré P.W., Wang S.M., Zhang J.L., Wu Y.N., Pang X.P., Xu W.B., Wang Z.L. (2014). Beneficial soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis (GB03) augments salt tolerance of white clover. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5: 525
Zhang J.L., Aziz M., Qiao Y., Han Q.Q., Li J., Wang Y.Q., Shen X., Wang S.M., Paré P.W. (2014). Soil microbe Bacillus subtilis (GB03) induces biomass accumulation and salt tolerance with lower sodium accumulation in wheat. Crop and Pasture Science, 65: 423-427
Zhang J.L., Flowers T.J., *Wang S.M. (2013) Differentiation of low-affinity Na+ uptake pathways and kinetics of the effects of K+ on Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant and Soil, 368: 629-640.
Kang J.J., Duan J.J., *Wang S.M., Zhao M., Yang Z.H. (2013). Na compound fertilizer promotes growth and enhances drought resistance of the succulent xerophyte Haloxylon ammodendron. Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 59:289-299.
Guo Q., Wang P., Ma Q., Zhang J.L., Bao A.K., *Wang S.M. (2012) Selective transport capacity for K+ over Na+ is linked to the expression levels of PtSOS1 in halophyte Puccinellia tenuiflora. Funct Plant Biol, 39: 1047-1057.
Ma Q., Yue L.J., Zhang J.L., Wu G.Q., Bao A.K., *Wang S.M. (2012) Sodium chloride improves photosynthesis and water status in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Tree Physiology, 32: 4-13.
Wu G.Q., Xi J.J., Wang Q., Bao A.K., Ma Q., Zhang J.L., *Wang S.M. (2011). The ZxNHX gene encoding tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter from the xerophytes Zygophyllum xanthoxylum plays important roles in response to salt and drought. Journal of Plant Physiology, 168: 758-767.
Lan W.Z., Wang W., Wang S.M., Li L.G., Buchanan B.B., Lin H.X., Gao J.P., Luan S. (2010). A rice high-affinity potassium transporter (HKT) from rice conceals a calcium-permeable cation channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107: 7089-7094.
Zhang J.L., Flowers T.J., *Wang S.M. (2010). Mechanisms of sodium uptake by roots of higher plants. Plant and Soil, 326:45-60.
Wang C.M., Zhang J.L., Liu X.S., Li Z., Wu G.Q., Cai J.Y., Flowers T.J., *Wang S.M. (2009) Puccinellia tenuiflora maintains a low Na+ level under salinity by limiting unidirectional Na+ influx resulting in a high selectivity for K+ over Na+. Plant, Cell and Environment, 32: 486-496.
Bao A.K., *Wang S.M., Wu G.Q., Xi J.J., Zhang J.L., Wang C.M. (2009) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis H+-PPase enhanced resistance to salt and drought stress in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Science, 176: 232-240.
Bao A.K., Guo Z.G., Zhang H.F., *Wang S.M. (2009). A procedure for assessing the salt tolerance of lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) cultivar seedlings by combining agronomic and physiological indicators. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 52: 435-443.
Wang S.M., Zhang J.L., *Flowers T. J. (2007) Low-affinity Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant Physiology 145: 559-571
Zhang H.F., *Wang S.M. (2007) Advances in study of Na+ uptake and transport in higher plants and Na+ homeostasis in the cell. Chinese Bulletin of Botany 24:561-571 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gong H. J., Zhu X. Y., Chen K. M., *Wang S.M., Zhang C. L. (2005) Silicon alleviates oxidative damage of wheat plants in pots under drought. Plant Science 169: 313-321
Zhu X. Y., Gong H. J., Chen G. C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C. L. (2005) Different solute levels in two spring wheat cultivars induced by progressive field water stress at different developmental stages. Journal of Arid Environments 62:1-14
*Wang S.M., Zhao G.Q., Gao Y.S., Tang Z.C., Zhang C.L. (2004) Puccinellia tenuiflora exhibits stronger selectivity for K+ over Na+ than wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition 27: 1841-1857
*Wang S.M., Wan C.G., Wang Y.R., Chen H., Zhou Z.Y., Fu H., Sosebee R.E. (2004) The Characteristics of Na+, K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. Journal of Arid Environments 56:525-539
Peng Y. H., Zhu Y. F., Mao Y. Q., Wang S.M., Su W. A., Tang Z.C. (2004) Alkali grass resists salt stress through high [K+] and an endodermis barrier to Na+. Journal of Experiment Botany 55: 939-949
Chen K.M., Gong H.J., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2004) The regulation of the plasma membrane redox system and H+-transport in adaptation of reed ecotypes to their habitats. Biologia Plantarum 48:87-92
Jing Y., Gong H.J., Zhao Z.G., Chen G.C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2004) Gradual drought under field conditions influences the glutathione metabolism, redox balance and energy supply in spring wheat. Acta Botanica Sinica 46:1040-1048
Chen K.M., Gong H.J., Chen G.C., Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2004) Gradual drought under field conditions influences the glutathione metabolism, redox balance and energy supply in spring wheat. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 23:20-28
Xing H., Tan L.L., An L.Z., Zhao Z.G., Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2004) Evidence for the involvement of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in osmotic stress tolerance of wheat seedlings: Inverse correlation between leaf abscisic acid accumulation and leaf water loss. Plant Growth Regulation 42:61-68
Gong H.J., Chen K.M., Chen G.C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Effects of silicon on growth of wheat under drought. Journal of Plant Nutrition 26:1055-1063
Gong H.J., Chen K.M., Chen G.C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Drought stress stimulates p-nitrophenyl phosphate hydrolysis rate of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase from wheat leaves. Plant Growth Regulation 40:139-145
Gong H.J., Chen K.M., Chen G.C., Zhao Z.G., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Redox system in the plasma membranes of two ecotypes of reed (Phragmites communis Trin.) leaves from different habitats. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 32:163-168
Zhu X.Y., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Composition and characteristic difference in photosynthetic membranes of two ecotypes of reed (Phragmites communis ) from different habitats. Photosynthetica 41:97-104
Zhu X.Y., Jing Y., Chen G.C., *Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Solute levels and osmoregulatory enzyme activities in reed plants adapted to drought and saline habitats. Plant Growth Regulation 41:165-172
Chen K.M., Gong H.J., Chen G.C., Wang S.M., Zhang C.L. (2003) Up-regulation of glutathione metabolism and changes in redox status involved in adaptation of reed (Phragmites communis Trin.) ecotypes to drought-prone and saline habitats. Journal of Plant Physiology 160: 293-301
*Wang S.M., Zheng W.J., Ren J.Z., Zhang C.L. (2002) Selectivity of various types of salt-resistant plants for K+ over Na+. Journal of Arid Environments 52:457-472
RESEARCH GRANTS:
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31730093). Jan. 2018 – Dec. 2022
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470503). Jan. 2015 – Dec. 2018
The National Basic Research Program of China (2014CB138701). Jan. 2014 –Aug. 2017
The Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20130211130001). Jan. 2014 – Dec. 2016
The National Agricultural Sci-Tech Transformation Foundation of China (2013GB2G100482). Jun. 2013 – Dec. 2015
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170431). Jan. 2012 – Dec. 2015
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31072073). Jan. 2011 – Dec. 2013
The National Agricultural Sci-Tech Transformation Foundation of China (2009GB23600512). Jun. 2009–Jun. 2011
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (30770347). Jan. 2008 – Dec. 2010
Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China ( 20090211110001) . Jan. 2009 – Dec. 2011
The National Basic Research Program of China (2007CB108901) (with Y.X. Yu) Jul. 2007 – Aug. 2011
The National High Tech Project of China (2006AA10Z126). Jan. 2007 – Dec. 2009
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (30671488). Jan. 2007 – Dec. 2009
The Program for New Century Excellent Talents, China (NCET-05-0882). Jan. 2006 – Dec. 2008
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (30270947). Jan. 2003 – Dec. 2005
The National Key Basic Pre-research Special Funds of MOST of China (2002CCC01600). Jan. 2003 – Dec. 2004
The National Science and Technology Plan Key Project of China (2001BA901A18). (with S.M. Gao) Jul. 2002 –Dec. 2004
The National Basic Research Program of China (G1999011705). (with C.L. Zhang) Jul. 2001 – Aug. 2004
The Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province in China (ZS041-A221-045-N). Jan. 2000 – Dec. 2002
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31730093). Jan. 2018 – Dec. 2022
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470503). Jan. 2015 – Dec. 2018
The National Basic Research Program of China (2014CB138701). Jan. 2014 –Aug. 2017
The Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20130211130001). Jan. 2014 – Dec. 2016
The National Agricultural Sci-Tech Transformation Foundation of China (2013GB2G100482). Jun. 2013 – Dec. 2015
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170431). Jan. 2012 – Dec. 2015
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31072073). Jan. 2011 – Dec. 2013
The National Agricultural Sci-Tech Transformation Foundation of China (2009GB23600512). Jun. 2009–Jun. 2011
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (30770347). Jan. 2008 – Dec. 2010
Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China ( 20090211110001) . Jan. 2009 – Dec. 2011
The National Basic Research Program of China (2007CB108901) (with Y.X. Yu) Jul. 2007 – Aug. 2011
The National High Tech Project of China (2006AA10Z126). Jan. 2007 – Dec. 2009
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (30671488). Jan. 2007 – Dec. 2009
The Program for New Century Excellent Talents, China (NCET-05-0882). Jan. 2006 – Dec. 2008
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (30270947). Jan. 2003 – Dec. 2005
The National Key Basic Pre-research Special Funds of MOST of China (2002CCC01600). Jan. 2003 – Dec. 2004
The National Science and Technology Plan Key Project of China (2001BA901A18). (with S.M. Gao) Jul. 2002 –Dec. 2004
The National Basic Research Program of China (G1999011705). (with C.L. Zhang) Jul. 2001 – Aug. 2004
The Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province in China (ZS041-A221-045-N). Jan. 2000 – Dec. 2002
AWARDS:
2012 Special government allowances of the State Council, China.
2011 The first prize of Natural Science in Gansu Province.
2009 The Leading Talent in Gansu Province.
2005 The Award for New Century Excellent Talents in University, the Ministry of Education of the P. R. China.
2003 The Sino-British Fellowship Trust Award of the Royal Society of the UK.
2002 Title of Outstanding Researcher in the Grassland Society of China.
2000 The International Exchange Award of the Royal Society of the UK.
1997, 1998, 2003, 2005, 2006 Progress Award in Science and Technology, the Government of Gansu Province, China.
1998 Progress Award in Science and Technology, the Ministry of Agriculture, China.
1995 Title of Outstanding Researcher in Gansu Grassland Ecological Research Institute.
1994 Outstanding Paper Award in the Chinese Society for Plant Physiology.
1994 Outstanding Paper Award in the Grassland Society of China.
2012 Special government allowances of the State Council, China.
2011 The first prize of Natural Science in Gansu Province.
2009 The Leading Talent in Gansu Province.
2005 The Award for New Century Excellent Talents in University, the Ministry of Education of the P. R. China.
2003 The Sino-British Fellowship Trust Award of the Royal Society of the UK.
2002 Title of Outstanding Researcher in the Grassland Society of China.
2000 The International Exchange Award of the Royal Society of the UK.
1997, 1998, 2003, 2005, 2006 Progress Award in Science and Technology, the Government of Gansu Province, China.
1998 Progress Award in Science and Technology, the Ministry of Agriculture, China.
1995 Title of Outstanding Researcher in Gansu Grassland Ecological Research Institute.
1994 Outstanding Paper Award in the Chinese Society for Plant Physiology.
1994 Outstanding Paper Award in the Grassland Society of China.
EDUCATION:
1995-1998 Ph.D. Plant Physiology, Gansu Agricultural University, China.
1987-1990 M.Sc. Plant Physiology and Genetics, Beijing Normal University, China.
1983-1987 B.Sc. Biology, Northwest Normal University, China.
1995-1998 Ph.D. Plant Physiology, Gansu Agricultural University, China.
1987-1990 M.Sc. Plant Physiology and Genetics, Beijing Normal University, China.
1983-1987 B.Sc. Biology, Northwest Normal University, China.
RESEARCH EXPERIENCE:
Jun.2004-Present: Professor, College of Pastoral Agriculture Science and Technology, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China.
Aug.2017-Feb.2018: Visiting Professor, Department of Biology and Institute of Biochemistry, Carleton University, Canada.
Collaborator: Professor Owen Rowland
Aug.2008- Jul.2009: Visiting Scholar, Department of Plant and Microbial Biology, University of California at Berkeley, USA.
Supervisor: Professor Sheng Luan
Feb.2003-Feb.2004: Research Fellow (supported by The Royal Society Sino-British Fellowship Trust Awards), School of Life Sciences, University of Sussex, UK.
Supervisor: Professor Tim Flowers
Sep.2000-May 2004: Associate Professor
College of Pastoral Agriculture Science and Technology, School of Life Science, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China.
Sep.1999-Aug.2000:Reaearch Visitor, National Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics, Shanghai Institute of Plant Physiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Jul.1998-Aug.1999: Postdoctoral fellow, School of Life Sciences, Lanzhou University
Supervisor: Prof. Cheng-Lie Zhang
Sep.1995-Jun.1998: Ph.D. thesis research, Gansu Agricultural University
Supervisor: Prof. Ji-Zhou Ren
Sep.1993-Aug.1995:Assistant Research Fellow, Gansu Grassland Ecological Research Institute (GGERI), Lanzhou, China.
Jul.1990-Aug.1993: Assistant, GGERI, Lanzhou, China.
Sep.1987-Jun.1990: M. Sc. thesis research, Department of Biology, Beijing Normal University
Supervisors: Prof. Wei-Ping Zhao and Prof. Si-Qi Zhao
Sep.1986-Jun.1987:B.Sc. thesis research, Department of Biology, Northwest Normal University
Supervisor: Prof. Si-Qi Zhao
Jun.2004-Present: Professor, College of Pastoral Agriculture Science and Technology, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China.
Aug.2017-Feb.2018: Visiting Professor, Department of Biology and Institute of Biochemistry, Carleton University, Canada.
Collaborator: Professor Owen Rowland
Aug.2008- Jul.2009: Visiting Scholar, Department of Plant and Microbial Biology, University of California at Berkeley, USA.
Supervisor: Professor Sheng Luan
Feb.2003-Feb.2004: Research Fellow (supported by The Royal Society Sino-British Fellowship Trust Awards), School of Life Sciences, University of Sussex, UK.
Supervisor: Professor Tim Flowers
Sep.2000-May 2004: Associate Professor
College of Pastoral Agriculture Science and Technology, School of Life Science, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China.
Sep.1999-Aug.2000:Reaearch Visitor, National Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics, Shanghai Institute of Plant Physiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Jul.1998-Aug.1999: Postdoctoral fellow, School of Life Sciences, Lanzhou University
Supervisor: Prof. Cheng-Lie Zhang
Sep.1995-Jun.1998: Ph.D. thesis research, Gansu Agricultural University
Supervisor: Prof. Ji-Zhou Ren
Sep.1993-Aug.1995:Assistant Research Fellow, Gansu Grassland Ecological Research Institute (GGERI), Lanzhou, China.
Jul.1990-Aug.1993: Assistant, GGERI, Lanzhou, China.
Sep.1987-Jun.1990: M. Sc. thesis research, Department of Biology, Beijing Normal University
Supervisors: Prof. Wei-Ping Zhao and Prof. Si-Qi Zhao
Sep.1986-Jun.1987:B.Sc. thesis research, Department of Biology, Northwest Normal University
Supervisor: Prof. Si-Qi Zhao